装配
目录
装配教程
本节的目的是演示如何使用装配和约束功能来构建真实的模型。它将是由 20x20 V 型槽型材制成的外壳门组件。
推荐 cadQuery 安装时使用 git 源安装,因为国内镜像源比如阿里、清华,可能没有同步最新版本(至少在小编测试时不是最新版本),导致部分代码无法正常运行,如 WorkPlane 里的 ancestors siblings 都在最新版本才有。
# 官方 git 安装
pip install git+https://github.com/CadQuery/cadquery.git
# git 无法访问的小伙伴,可以使用 gitee 安转
pip install git+https://gitee.com/zjf_lyy/cadquery.git定义参数
我们希望从定义模型参数开始,以便稍后轻松更改尺寸:
import cadquery as cq
# Parameters
H = 400
W = 200
D = 350
PROFILE = cq.importers.importDXF("vslot-2020_1.dxf").wires()
SLOT_D = 5
PANEL_T = 3
HANDLE_D = 20
HANDLE_L = 50
HANDLE_W = 4值得注意的是,V 型槽轮廓是从 DXF 文件导入的。这样就很容易改用其他铝型材类型,如 e.g. Item 或 Bosch。供应商通常会提供 DXF 文件。
定义可重用组件
接下来,我们要定义根据指定参数生成装配组件的函数。
def make_vslot(l):
return PROFILE.toPending().extrude(l)
def make_connector():
rv = (
cq.Workplane()
.box(20, 20, 20)
.faces("<X")
.workplane()
.cboreHole(6, 15, 18)
.faces("<Z")
.workplane(centerOption="CenterOfMass")
.cboreHole(6, 15, 18)
)
# tag mating faces
rv.faces(">X").tag("X").end()
rv.faces(">Z").tag("Z").end()
return rv
def make_panel(w, h, t, cutout):
rv = (
cq.Workplane("XZ")
.rect(w, h)
.extrude(t)
.faces(">Y")
.vertices()
.rect(2 * cutout, 2 * cutout)
.cutThruAll()
.faces("<Y")
.workplane()
.pushPoints([(-w / 3, HANDLE_L / 2), (-w / 3, -HANDLE_L / 2)])
.hole(3)
)
# tag mating edges
rv.faces(">Y").edges("%CIRCLE").edges(">Z").tag("hole1")
rv.faces(">Y").edges("%CIRCLE").edges("<Z").tag("hole2")
return rv
def make_handle(w, h, r):
pts = ((0, 0), (w, 0), (w, h), (0, h))
path = cq.Workplane().polyline(pts)
rv = (
cq.Workplane("YZ")
.rect(r, r)
.sweep(path, transition="round")
.tag("solid")
.faces("<X")
.workplane()
.faces("<X", tag="solid")
.hole(r / 1.5)
)
# tag mating faces
rv.faces("<X").faces(">Y").tag("mate1")
rv.faces("<X").faces("<Y").tag("mate2")
return rv初始组装
接下来,我们要实例化所有组件,并将它们添加到装配体中。
# define the elements
door = (
cq.Assembly()
.add(make_vslot(H), name="left")
.add(make_vslot(H), name="right")
.add(make_vslot(W), name="top")
.add(make_vslot(W), name="bottom")
.add(make_connector(), name="con_tl", color=cq.Color("black"))
.add(make_connector(), name="con_tr", color=cq.Color("black"))
.add(make_connector(), name="con_bl", color=cq.Color("black"))
.add(make_connector(), name="con_br", color=cq.Color("black"))
.add(
make_panel(W + SLOT_D, H + SLOT_D, PANEL_T, SLOT_D),
name="panel",
color=cq.Color(0, 0, 1, 0.2),
)
.add(
make_handle(HANDLE_D, HANDLE_L, HANDLE_W),
name="handle",
color=cq.Color("yellow"),
)
)约束定义
然后,我们要定义所有的约束条件
# define the constraints
(
door
# left profile
.constrain("left@faces@<Z", "con_bl?Z", "Plane")
.constrain("left@faces@<X", "con_bl?X", "Axis")
.constrain("left@faces@>Z", "con_tl?Z", "Plane")
.constrain("left@faces@<X", "con_tl?X", "Axis")
# top
.constrain("top@faces@<Z", "con_tl?X", "Plane")
.constrain("top@faces@<Y", "con_tl@faces@>Y", "Axis")
# bottom
.constrain("bottom@faces@<Y", "con_bl@faces@>Y", "Axis")
.constrain("bottom@faces@>Z", "con_bl?X", "Plane")
# right connectors
.constrain("top@faces@>Z", "con_tr@faces@>X", "Plane")
.constrain("bottom@faces@<Z", "con_br@faces@>X", "Plane")
.constrain("left@faces@>Z", "con_tr?Z", "Axis")
.constrain("left@faces@<Z", "con_br?Z", "Axis")
# right profile
.constrain("right@faces@>Z", "con_tr@faces@>Z", "Plane")
.constrain("right@faces@<X", "left@faces@<X", "Axis")
# panel
.constrain("left@faces@>X[-4]", "panel@faces@<X", "Plane")
.constrain("left@faces@>Z", "panel@faces@>Z", "Axis")
# handle
.constrain("panel?hole1", "handle?mate1", "Plane")
.constrain("panel?hole2", "handle?mate2", "Point")
)如果您需要做一些使用字符串选择器无法实现的特殊操作(例如使用cadquery.selectors.BoxSelector或用户定义的选择器类),可以将cadquery.Shape对象直接传递给cadquery.Assembly.constrain()方法。例如上面的
.constrain("part1@faces@>Z", "part3@faces@<Z", "Axis")相当于
.constrain("part1", part1.faces(">z").val(), "part3", part3.faces("<Z").val(), "Axis")此方法需要一个cadquery.Shape对象,因此请记住使用该cadquery.Workplane.val() 方法传递单个cadquery.Shape对象,而不是整个cadquery.Workplane对象。
最后结果
下面是完整的代码,包括最后的求解步骤。
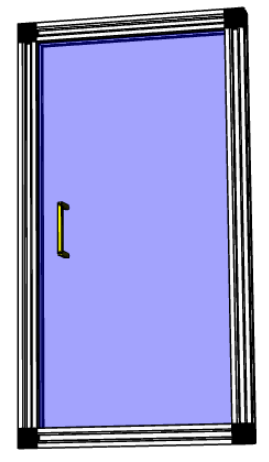

import cadquery as cq
# Parameters
H = 400
W = 200
D = 350
# 文件可以在 https://gitee.com/zjf_lyy/cadquery.git 中下载 /doc/vslot-2020_1.dxf
# 下载地址 https://gitee.com/zjf_lyy/cadquery/raw/master/doc/vslot-2020_1.dxf
PROFILE = cq.importers.importDXF("vslot-2020_1.dxf").wires()
SLOT_D = 6
PANEL_T = 3
HANDLE_D = 20
HANDLE_L = 50
HANDLE_W = 4
def make_vslot(l):
return PROFILE.toPending().extrude(l)
def make_connector():
rv = (
cq.Workplane()
.box(20, 20, 20)
.faces("<X")
.workplane()
.cboreHole(6, 15, 18)
.faces("<Z")
.workplane(centerOption="CenterOfMass")
.cboreHole(6, 15, 18)
)
# tag mating faces
rv.faces(">X").tag("X").end()
rv.faces(">Z").tag("Z").end()
return rv
def make_panel(w, h, t, cutout):
rv = (
cq.Workplane("XZ")
.rect(w, h)
.extrude(t)
.faces(">Y")
.vertices()
.rect(2 * cutout, 2 * cutout)
.cutThruAll()
.faces("<Y")
.workplane()
.pushPoints([(-w / 3, HANDLE_L / 2), (-w / 3, -HANDLE_L / 2)])
.hole(3)
)
# tag mating edges
rv.faces(">Y").edges("%CIRCLE").edges(">Z").tag("hole1")
rv.faces(">Y").edges("%CIRCLE").edges("<Z").tag("hole2")
return rv
def make_handle(w, h, r):
pts = ((0, 0), (w, 0), (w, h), (0, h))
path = cq.Workplane().polyline(pts)
rv = (
cq.Workplane("YZ")
.rect(r, r)
.sweep(path, transition="round")
.tag("solid")
.faces("<X")
.workplane()
.faces("<X", tag="solid")
.hole(r / 1.5)
)
# tag mating faces
rv.faces("<X").faces(">Y").tag("mate1")
rv.faces("<X").faces("<Y").tag("mate2")
return rv
# define the elements
door = (
cq.Assembly()
.add(make_vslot(H), name="left")
.add(make_vslot(H), name="right")
.add(make_vslot(W), name="top")
.add(make_vslot(W), name="bottom")
.add(make_connector(), name="con_tl", color=cq.Color("black"))
.add(make_connector(), name="con_tr", color=cq.Color("black"))
.add(make_connector(), name="con_bl", color=cq.Color("black"))
.add(make_connector(), name="con_br", color=cq.Color("black"))
.add(
make_panel(W + 2 * SLOT_D, H + 2 * SLOT_D, PANEL_T, SLOT_D),
name="panel",
color=cq.Color(0, 0, 1, 0.2),
)
.add(
make_handle(HANDLE_D, HANDLE_L, HANDLE_W),
name="handle",
color=cq.Color("yellow"),
)
)
# define the constraints
(
door
# left profile
.constrain("left@faces@<Z", "con_bl?Z", "Plane")
.constrain("left@faces@<X", "con_bl?X", "Axis")
.constrain("left@faces@>Z", "con_tl?Z", "Plane")
.constrain("left@faces@<X", "con_tl?X", "Axis")
# top
.constrain("top@faces@<Z", "con_tl?X", "Plane")
.constrain("top@faces@<Y", "con_tl@faces@>Y", "Axis")
# bottom
.constrain("bottom@faces@<Y", "con_bl@faces@>Y", "Axis")
.constrain("bottom@faces@>Z", "con_bl?X", "Plane")
# right connectors
.constrain("top@faces@>Z", "con_tr@faces@>X", "Plane")
.constrain("bottom@faces@<Z", "con_br@faces@>X", "Plane")
.constrain("left@faces@>Z", "con_tr?Z", "Axis")
.constrain("left@faces@<Z", "con_br?Z", "Axis")
# right profile
.constrain("right@faces@>Z", "con_tr@faces@>Z", "Plane")
.constrain("right@faces@<X", "left@faces@<X", "Axis")
# panel
.constrain("left@faces@>X[-4]", "panel@faces@<X", "Plane")
.constrain("left@faces@>Z", "panel@faces@>Z", "Axis")
# handle
.constrain("panel?hole1", "handle?mate1", "Plane")
.constrain("panel?hole2", "handle?mate2", "Point")
)
# solve
door.solve()
show_object(door, name="door")数据导出
生成的装配体可导出为 STEP 文件或内部 OCCT XML 格式
STEP 可以加载到所有 CAD 工具中,例如 FreeCAD 中,XML 可以用在使用 OCCT 的应用程序中。
1 door.save("door.step")
2 door.save("door.xml")
对象位置
对象可根据提供的初始位置添加到装配体中,例如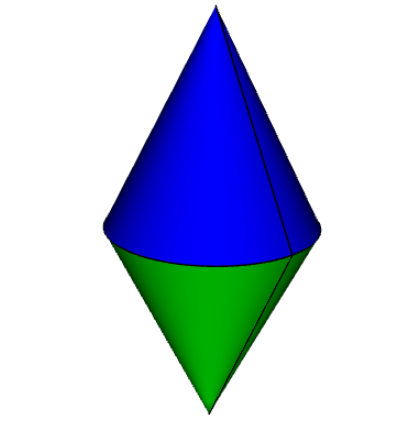
import cadquery as cq
cone = cq.Solid.makeCone(1, 0, 2)
assy = cq.Assembly()
assy.add(
cone,
loc=cq.Location((0, 0, 0), (1, 0, 0), 180),
name="cone0",
color=cq.Color("green"),
)
assy.add(cone, name="cone1", color=cq.Color("blue"))
show_object(assy)除了用户计算位置外,还可以使用约束条件和方法 solve()来定位装配体中的对象。
如果使用了初始位置和解算方法 solve(),求解器将使用其解决方案覆盖这些初始位置,然而初始位置仍然可能影响最终的解决方案。在约束不足的系统中,如果某个对象对成本函数没有贡献,求解器可能不会移动该对象,或者如果存在多个解决方案(即成本函数为最小值的多个实例),初始位置可能会导致求解器收敛于一个特定的解决方案。对于非常复杂的装配体,设置近似正确的初始位置也可以减少所需的计算时间。
Constraints 约束条件
与直接提供位置相比,约束通常可以更好地表示用户想要建模的现实世界关系。在上面的示例中,现实世界的关系是每个圆锥体的底面应该接触,可以使用平面约束对其进行建模。当用户提供明确的位置(而不是约束)时,他们还有责任在位置发生cone1变化时更新它们。
当提供至少一个约束并solve()运行该方法时,就会建立一个优化问题。每个约束都提供一个成本函数,该函数取决于Location创建约束时指定的两个对象的位置和方向(由 a 表示)。解算器会改变装配体子项的位置,并尝试最小化所有成本函数的总和。因此,通过阅读下面的成本函数公式,您可以准确理解每个约束的作用。
Point
点约束是一种常用的约束条件,它能使两点之间的距离最小化。一些示例用途包括面居中或顶点对齐,但它也可用于虚顶点,在两个部件之间创建偏移。
The cost function is: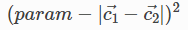
Where:
创建点约束时,param参数可用于指定两个中心之间所需的偏移量。该偏移量没有与之关联的方向,如果您想指定特定方向的偏移量,那么您应该使用虚拟顶点 Vertex。
Point 约束使用Center()来查找参数的中心。因此它将适用于的所有子类Shape。
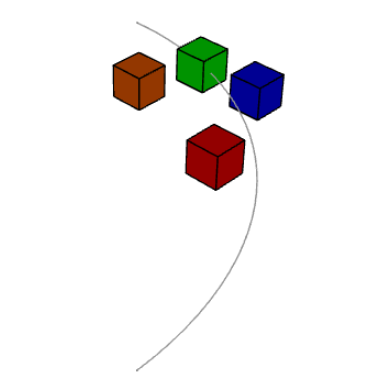
import cadquery as cq
# Use the Point constraint to position boxes relative to an arc
line = cq.Edge.makeCircle(radius=10, angle1=0, angle2=90)
box = cq.Workplane().box(1, 1, 1)
assy = cq.Assembly()
assy.add(line, name="line")
# position the red box on the center of the arc
assy.add(box, name="box0", color=cq.Color("red"))
assy.constrain("line", "box0", "Point")
# position the green box at a normalized distance of 0.8 along the arc
position0 = line.positionAt(0.8)
assy.add(box, name="box1", color=cq.Color("green"))
assy.constrain(
"line",
cq.Vertex.makeVertex(*position0.toTuple()),
"box1",
box.val(),
"Point",
)
# position the orange box 2 units in any direction from the green box
assy.add(box, name="box2", color=cq.Color("orange"))
assy.constrain(
"line",
cq.Vertex.makeVertex(*position0.toTuple()),
"box2",
box.val(),
"Point",
param=2,
)
# position the blue box offset 2 units in the x direction from the green box
position1 = position0 + cq.Vector(2, 0, 0)
assy.add(box, name="box3", color=cq.Color("blue"))
assy.constrain(
"line",
cq.Vertex.makeVertex(*position1.toTuple()),
"box3",
box.val(),
"Point",
)
assy.solve()
show_object(assy)Axis
轴约束最小化两个矢量之间的夹角。它常用于对齐面和控制物体的旋转。
The cost function is: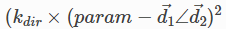
Where:
该参数param默认为 180 度,这将两个方向设置为彼此相反。也就是通常所说的“配对”关系,即两个物体的外表面接触。

import cadquery as cq
cone = cq.Solid.makeCone(1, 0, 2)
assy = cq.Assembly()
assy.add(cone, name="cone0", color=cq.Color("green"))
assy.add(cone, name="cone1", color=cq.Color("blue"))
assy.constrain("cone0@faces@<Z", "cone1@faces@<Z", "Axis")
assy.solve()
show_object(assy)如果param参数设置为零,则两个对象将指向同一方向。当一个物体穿过另一个物体时,例如一根大头针插入板上的孔中,通常会使用这种方法: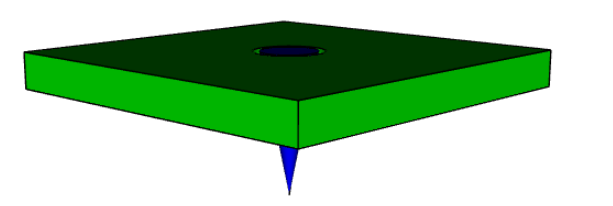
import cadquery as cq
plate = cq.Workplane().box(10, 10, 1).faces(">Z").workplane().hole(2)
cone = cq.Solid.makeCone(0.8, 0, 4)
assy = cq.Assembly()
assy.add(plate, name="plate", color=cq.Color("green"))
assy.add(cone, name="cone", color=cq.Color("blue"))
# place the center of the flat face of the cone in the center of the upper face of the plate
assy.constrain("plate@faces@>Z", "cone@faces@<Z", "Point")
# set both the flat face of the cone and the upper face of the plate to point in the same direction
assy.constrain("plate@faces@>Z", "cone@faces@<Z", "Axis", param=0)
assy.solve()
show_object(assy)在创建轴Axis约束时,根据对象的类型,以三种不同方式之一提取方向向量。Face:使用normalAt()Edge并且geomType()是"CIRCLE":使用normal()Edge并且geomType()不是"CIRCLE":使用tangentAt()
使用任何其他类型的对象都会引发ValueError. 到目前为止,最常见的用例是从Face.
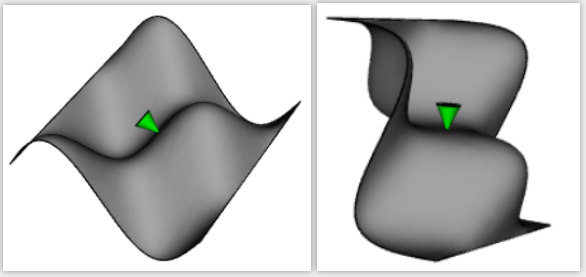
import cadquery as cq
from math import cos, sin, pi
# Create a sinusoidal surface:
surf = cq.Workplane().parametricSurface(
lambda u, v: (u, v, 5 * sin(pi * u / 10) * cos(pi * v / 10)),
N=40,
start=0,
stop=20,
)
# Create a cone with a small, flat tip:
cone = (
cq.Workplane()
.add(cq.Solid.makeCone(1, 0.1, 2))
# tag the tip for easy reference in the constraint:
.faces(">Z")
.tag("tip")
.end()
)
assy = cq.Assembly()
assy.add(surf, name="surf", color=cq.Color("lightgray"))
assy.add(cone, name="cone", color=cq.Color("green"))
# set the Face on the tip of the cone to point in
# the opposite direction of the center of the surface:
assy.constrain("surf", "cone?tip", "Axis")
# to make the example clearer, move the cone to the center of the face:
assy.constrain("surf", "cone?tip", "Point")
assy.solve()
show_object(assy)Plane
平面约束是点约束和轴约束的简单组合。它是常用约束组合的便捷快捷方式。用它可以将上例中的两个限制条件缩短为一个:
assy = cq.Assembly()
assy.add(surf, name="surf", color=cq.Color("lightgray"))
assy.add(cone, name="cone", color=cq.Color("green"))
-# set the Face on the tip of the cone to point in
-# the opposite direction of the center of the surface:
-assy.constrain("surf", "cone?tip", "Axis")
-# to make the example clearer, move the cone to the center of the face:
-assy.constrain("surf", "cone?tip", "Point")
+assy.constrain("surf", "cone?tip", "Plane")
assy.solve()
show_object(assy)这段代码的结果与上述两个约束示例完全相同。
Plane 的成本函数请参见 Point 和 Axis 部分。该param参数应用于轴,应保留为“mate”样式约束(两个表面接触)的默认值,或者可设置为 0以实现贯通面约束(请参阅轴约束部分中的说明)。
PointInPlane
PointInPlane 将第一个对象的中心定位在第二个对象定义的平面内。
The cost function is: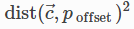
Where:
(images/demo-dog.png)

import cadquery as cq
# Create an L-shaped object:
bracket = (
cq.Workplane("YZ")
.hLine(1)
.vLine(0.1)
.hLineTo(0.2)
.vLineTo(1)
.hLineTo(0)
.close()
.extrude(1)
# tag some faces for easy reference:
.faces(">Y[1]")
.tag("inner_vert")
.end()
.faces(">Z[1]")
.tag("inner_horiz")
.end()
)
box = cq.Workplane().box(0.5, 0.5, 0.5)
assy = cq.Assembly()
assy.add(bracket, name="bracket", color=cq.Color("gray"))
assy.add(box, name="box", color=cq.Color("green"))
# lock bracket orientation:
assy.constrain("bracket@faces@>Z", "box@faces@>Z", "Axis", param=0)
assy.constrain("bracket@faces@>X", "box@faces@>X", "Axis", param=0)
# constrain the bottom of the box to be on the plane defined by inner_horiz:
assy.constrain("box@faces@<Z", "bracket?inner_horiz", "PointInPlane")
# constrain the side of the box to be 0.2 units from the plane defined by inner_vert
assy.constrain("box@faces@<Y", "bracket?inner_vert", "PointInPlane", param=0.2)
# constrain the end of the box to be 0.1 units inside the end of the bracket
assy.constrain("box@faces@>X", "bracket@faces@>X", "PointInPlane", param=-0.1)
assy.solve()
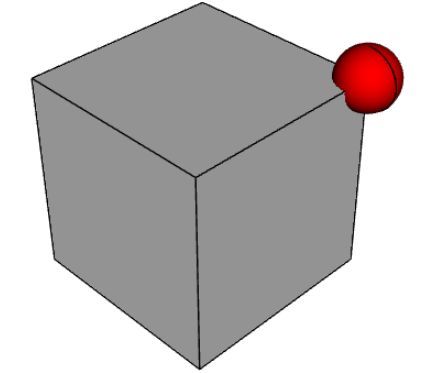
show_object(assy)PointOnLine
PointOnLine 将第一个对象的中心定位在第二个对象定义的线上。
The cost function is: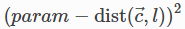
Where:
import cadquery as cq
b1 = cq.Workplane().box(1, 1, 1)
b2 = cq.Workplane().sphere(0.15)
assy = (
cq.Assembly()
.add(b1, name="b1")
.add(b2, loc=cq.Location((0, 0, 4)), name="b2", color=cq.Color("red"))
)
# fix the position of b1
assy.constrain("b1", "Fixed")
# b2 on one of the edges of b1
assy.constrain("b2", "b1@edges@>>Z and >>Y", "PointOnLine")
# b2 on another of the edges of b1
assy.constrain("b2", "b1@edges@>>Z and >>X", "PointOnLine")
# effectively b2 will be constrained to be on the intersection of the two edges
assy.solve()
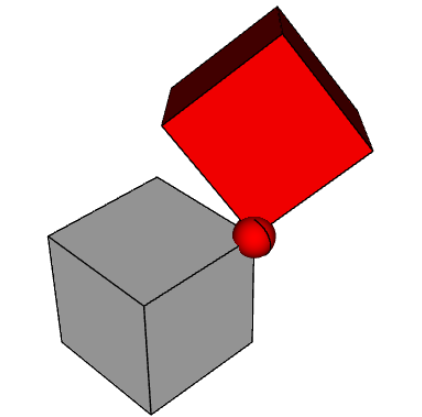
show_object(assy)FixedPoint
FixPoint 将给定参数的位置固定为等于通过约束参数指定的给定点。该约束锁定了参数的所有平移自由度。
The cost function is: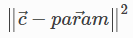
Where:
import cadquery as cq
b1 = cq.Workplane().box(1, 1, 1)
b2 = cq.Workplane().sphere(0.15)
assy = (
cq.Assembly()
.add(b1, name="b1")
.add(b2, loc=cq.Location((0, 0, 4)), name="b2", color=cq.Color("red"))
.add(b1, loc=cq.Location((-2, 0, 0)), name="b3", color=cq.Color("red"))
)
pnt = (0.5, 0.5, 0.5)
# fix the position of b1
assy.constrain("b1", "Fixed")
# fix b2 center at point
assy.constrain("b2", "FixedPoint", pnt)
# fix b3 vertex position at point
assy.constrain("b3@vertices@<X and <Y and <Z", "FixedPoint", pnt)
assy.solve()
show_object(assy)FixedRotation
FixRotation 将给定参数的旋转固定为等于通过约束参数指定的值。
此约束锁定参数的所有旋转自由度。
The cost function is: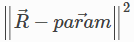
Where:

import cadquery as cq
b1 = cq.Workplane().box(1, 1, 1)
b2 = cq.Workplane().rect(0.1, 0.1).extrude(1, taper=-15)
assy = (
cq.Assembly()
.add(b1, name="b1")
.add(b2, loc=cq.Location((0, 0, 4)), name="b2", color=cq.Color("red"))
)
# fix the position of b1
assy.constrain("b1", "Fixed")
# fix b2 bottom face position (but not rotation)
assy.constrain("b2@faces@<Z", "FixedPoint", (0, 0, 0.5))
# fix b2 rotational degrees of freedom too
assy.constrain("b2", "FixedRotation", (45, 0, 45))
assy.solve()
show_object(assy)FixedAxis
FixAxis 将给定参数的法线或切线的方向固定为等于通过约束参数指定的向量的方向。
此约束锁定参数的两个旋转自由度。
成本函数为:
在哪里:

import cadquery as cq
b1 = cq.Workplane().box(1, 1, 1)
b2 = cq.Workplane().rect(0.1, 0.1).extrude(1, taper=-15)
assy = (
cq.Assembly()
.add(b1, name="b1")
.add(b2, loc=cq.Location((0, 0, 4)), name="b2", color=cq.Color("red"))
)
# fix the position of b1
assy.constrain("b1", "Fixed")
# fix b2 bottom face position (but not rotation)
assy.constrain("b2@faces@<Z", "FixedPoint", (0, 0, 0.5))
# fix b2 some rotational degrees of freedom too
assy.constrain("b2@faces@>Z", "FixedAxis", (1, 0, 2))
assy.solve()
show_object(assy)Assembly colors 装配颜色
除了 RGBA 值之外,该类Color还可以使用文本名称来实例化。下面列出了有效名称以及颜色示例:
最后编辑:码峰 更新时间:2024-01-12 17:58


